Right-click the agent node for which you want to create a new instance, click All Tasks, and then click New PostGreSQL Server.

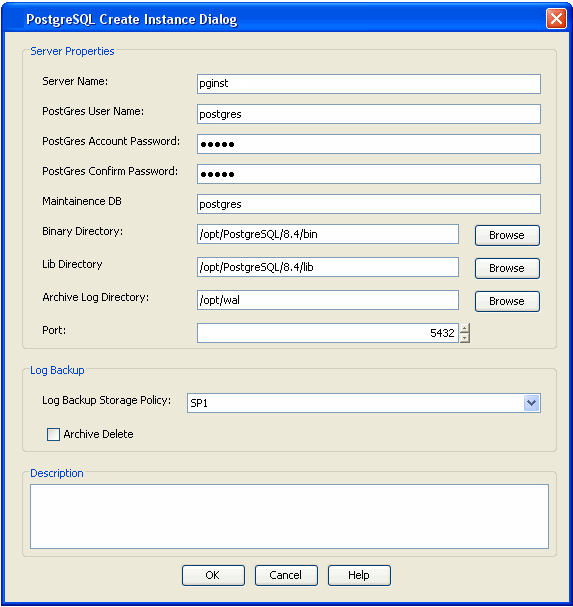
- Enter the name of PostgreSQL Server in Server Name.
- Type the user name to access the PostGres application on a Unix
client in the PostGres User Name
box.
In order to create a PostGreSQL instance, the PostGreSQL user should have Administrator (DBA) and System Administrator (SYSDBA) privileges. Make sure that you have database administrator privileges to access the application.
- Type the PostGres User Account Password and Confirm the Password in PostGres Account Password and PostGres Confirm Password boxes.
- Type the name of a system database which is used as Maintenance DB. A Maintenance database is used for connecting PostGreSQL server. Any database that exists on PostgreSQL can be selected as a Maintenance database.This database should exist in the PostGreSQL server. The Backups and Restores will fail, if the Maintenance database is not existing or dropped.
- Type the path to the PostGres application files in the Binary Directory box or click Browse to locate the path. For example, /opt/PostgreSQL/8.4/bin.Make sure to avoid using special characters such as slash(/), underscore(_), and spaces.
- Type the path to the library directory for the instance in the
Lib Directory box or click Browse to locate the path.
For example, /opt/PostgreSQL/8.4/lib
Postgres Lib directory path must contain libpq.so file and other related files. This library is used to connect to the database and execute queries. Execute the following command from the bin directory to locate required library path:
pg_config --libdir
For example:
bash-3.2$ cd /opt/PostgreSQL/8.4/bin
bash-3.2$./pg_config --libdir
bash-3.2$ /opt/PostgreSQL/8.4/lib
- A separate directory should be created for archive log
directory. Type the path to this archive log directory for the instance in
the
Archive Log Directory box or click Browse to locate
the path. Make sure that this path does not point to the pg_log
and pg_xlog
directories. You should have the database administrator privileges
(r-w-x) to
access this directory.
For example, /opt/wal
From PostgreSQL 8.3 version onwards, use the following command to turn on the archive_mode. This feature is not supported for PostgreSQL 8.2 and earlier versions. Also, specify this path in the postgresql.conf file prior to performing the PostgreSQL FS backup.
archive_mode = on
archive_command = 'cp %p /opt/wal/%f'From PostGreSQL 9.x.x version onwards, use the following configuration:
Set wal_level = archive instead of default wal_level = minimal
- Select the Port to open the communication between PostGreSQL Server and Clients.
- Select the Log Backup Storage Policy to be used for the transaction log backup jobs under Log Backup section.
- Select Archive Delete, if you need to delete the archived log backup files.
Refer Troubleshooting for any issues during the creation of an instance.
The backupsets and subclients necessary for your backup operation are automatically created by default, once you create an instance.
