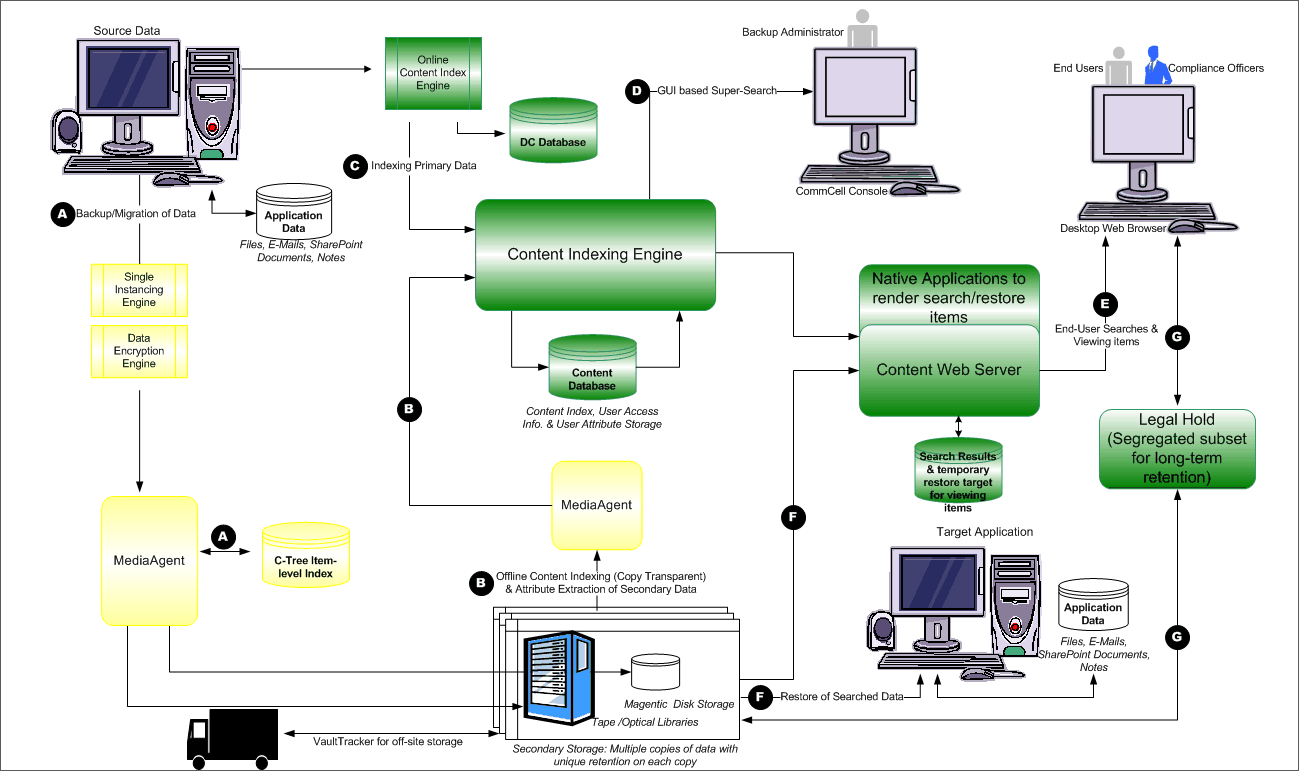
Content Indexing and Search consists of the following main components.
The diagram on the right provides a broad overview of the deployment and
configuration of these components.
-
The Content Indexing Engine is the core component for the content
indexing and search feature. It is the underlying integrated software
application that provides indexing, searching and filtering services for all
data - including file server/desktop data and protected/archived data - in the CommCell. As the content
indexing process is very resource intensive it is recommended that the
engine be installed in powerful computer that has extensive memory and hard
disk availability at all times. (See
System Requirements - Content
Indexing Engine for minimum requirements.)
The Content Indexing Engine may be installed as a single-node
installation where all the components within the Content Indexing Engine are
installed in the same computer. Depending on the volume of data that must be
content indexed in a CommCell, one or more Content Indexing Engines can be
installed and configured.
You can also perform a multi-node install to customize the installation
of each Content indexing Engine to distribute and harness the capacity of
multiple computers.
Content Indexing Engine is the first component that must be installed.
(See Deployment - Content Indexing and
Search for more information on how to install the Content Indexing
Engine.) The properties of each Content Indexing Engine in the CommCell is
displayed in the CommCell Console under Storage Resources. Both
offline and online content indexing processes are configured to use a
Content Indexing Engine. This is explained in the following sections.
-
Offline Content Indexing is used to content index the storage data
secured by the various data protection/data archive operations. For this reason the configuration of the
Offline Content Indexing is associated with a storage policy. Each storage policy must be
configured to use a Content Indexing Engine, if content indexing is enabled
in the storage policy. (See
Configuration - Content indexing and Search for more details.) The
MediaAgent associated with the Storage Policy will be used for reading the
data associated with the storage policy.
Offline content indexing is supported for all types of of data including
compressed, deduplicated and encrypted data.
Offline Content Indexing for NAS NDMP Agents
Offline content indexing is also supported for NAS NDMP backups. See
Content
Indexing- Support for a list of data types that are supported by offline content
indexing.
In order to view or restore the content indexed NAS NDMP data from the
Search Console, install the
File System NDMP Restore Enabler on the web search server.
Offline Content Indexing for Virtual Server
iDataAgent
Offline content indexing is also supported for file level backups on
virtual servers. See
Content
Indexing- Support to know the virtual server platforms supported by
offline content indexing.
-
Online Content Indexing operations can be
performed using the following agents:
Online Content Indexing for File System Agent
The Online Content Indexing for File System Agent allows you to content
index live files residing on Windows computers.
Online Content Indexing for Exchange Agent
The Online Content Indexing for Exchange Agent allows you to content
index the following data types:
- Mailboxes
- Folders within a mailbox
- Messages within a folder
- Attachments
The Online Content Indexing
Agents must be installed on all the computers in the CommCell that you wish
to content index and search. See Deployment - Content Indexing and
Search for information on installing the Online Content
Indexing agents.
This agent can use the Data Classification Enabler to
facilitate content indexing the data.
See Configuration - Content indexing and Search for
information on configuring the Online Content
Indexing agents.
-
Once the data is content indexed, it can be searched for data discovery
and other purposes. Search can be performed using the following components:
-
The web-based Search Console provides a multi-purpose and flexible method to
search and if necessary restore data. It has an easy-to-use search interface
modeled after popular search engines. The Search Console also has powerful
built-in security features that enables both compliance and end-users to
search data based on individual security permissions. In addition, it
also allows users to restore the appropriate file/data if necessary.
The Search Console provides several options and tools to search the
data. It also allows users to preview the search results in the same or
new window. When performing end-user search, the Search Console also provides
options to search for Exchange emails on delegated mailboxes for a specific user.
This is described in
Data Discovery
and Search. For information on installing the Web Search Server, see Deployment - Content Indexing and
Search.
In order to view or restore the content indexed NAS NDMP data from the
Search Console, install the
File System NDMP Restore Enabler on the web search server.
Once installed, the web-based
Search Console and User security must be configured before it is used. See
Configuration - Content
indexing and Search for more information.
-
The CommCell Console also has the ability to Search and Restore data
based on User Security defined in the CommCell. See
Data Discovery
and Search for more information. However, note that the CommCell
Console does not provide the end-user search capability which is
provided by the web-based Search Console. The CommCell Console also
provides the facility to preview the search results in a preview pane.
For more information, see
Data Discovery
and Search.
-
Legal Hold provides the ability for a compliance user to segregate
relevant information found during a data discovery and search operation and
preserve them for long term retention for legal purposes. It uses a policy
based approach to search relevant data and retain a subset of the data for a long retention period.
Legal Holds can be created from the Search Console as well as the CommCell
Console.
-
Search Console
The Search Console
provides the facility to add the search items to a new Legal Hold or to an
existing Legal Hold interactively. The items added to the Legal Hold will be an unaltered
copy of the original data.
The Search Console also provides the facility to modify or delete an
existing Legal Hold. Once the Legal Hold is created, you can retrieve the
Legal Hold items to a new review set. For detailed information, see
Legal Hold.
-
CommCell Console
Legal Holds can be created, modified, and deleted from the CommCell
Console. In addition, you can also automate and schedule the process of
adding discovered items to a new or existing Legal Hold using the Automated
Content Classification Policy.
Whenever a new Legal Hold is created, a corresponding
Legal Hold Set is
automatically created under the CommServe's File System
iDataAgent in the CommCell Console.
You can retrieve data from the Legal Hold Set in the CommCell Console. For
more information, see
Legal Hold.
-
When performing search on content indexed data, you can assign tags
to the discovered items for easy identification/classification. These tagged
items can then be searched based on the tags. There are pre-defined tags or
system tags already available in the CommServe. In addition, you can also
create user-defined tags from the CommCell Console.
Tagging is applicable only for Compliance users and administrators.
-
Search Console
The Search Console provides the facility to assign tags to search items
interactively. The associated tags are automatically displayed on the search
result page as well as the review set page for each search item. You can
also perform search based on the associated tags.
-
CommCell Console
Tags are defined from the CommCell Console. There are also pre-defined
tags created and stored in the CommServe database by default. These tags are
readily available for tagging purposes. A compliance user can create,
modify, or delete user-defined tags from the CommCell Console. Once created,
you can schedule the operation of assigning tags to search items using the
Automated Content Classification Policy in the CommCell Console.
For detailed information on creating and assigning tags, see
Tagging.
-
ERM (Enterprise Records Management) Connectors allows you to submit
discovered documents and files to a record management system.
Currently, the software supports submission of documents to Microsoft
SharePoint Record Center. When you create an ERM Connector, you
pre-define the mapping of documents to a specific ERM server in the
record management site. ERM Connectors can be used only by Compliance users.
You can create and use ERM Connectors from the Search Console as well as the
CommCell Console.
-
Search Console
Once you have moved the search result items to a review set, you can
select specific search items in the review set and submit them to an ERM
using available ERM Connectors interactively. You can also create a new ERM
Connector and map it to an existing or new ERM server in the record
management site from the Search Console.
-
CommCell Console
In addition to creating ERM Connectors, you can modify or delete ERM
Connectors from the CommCell Console. You can also schedule the process of
submitting content indexed documents to the Records Management Site using
the Automated Content Classification Policy.
For detailed information on using ERM Connectors, see
Enterprise Records
Management (ERM).
-
The Automated Content Classification Policy is a component under
Content Director node in the CommCell
Console, that allows you to automate and schedule the data discovery
and search operations, such as Legal Hold, Tagging, Restore to
Review Set, and ERM
Connector. You can also use the policy to restore the discovered
items
to a review set in the Web Search Server. When automating these
operations, you can also specify the date from which the
backup/archive data will be considered for the search. If a
particular job is qualified to be processed by the Automated Content
Classification Policy, it will be not be pruned even though eligible to be pruned,
until acted upon by the policy. For more information, see
Automated Content
Classification Policy.
|